Become an Accountant: A Step-by-Step Guide
Embarking on a career in accounting can be a rewarding and challenging profession. As we explore the world of finance, we find that accountants play a vital role in ensuring the financial health of businesses and organizations.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, accountants earn a median annual salary of $78,000 as of 2022, significantly above the national average. With a projected 4% job growth between 2022 and 2032, the demand for skilled accountants is on the rise.
To succeed in this field, one must understand the education and degree requirements, as well as the necessary steps to become a certified accountant. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of building a successful career in accounting.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the role of accountants in business and finance
- Exploring the educational requirements for a career in accounting
- Learning the steps to become a certified accountant
- Discovering the career advancement opportunities in accounting
- Understanding the impact of technology on the accounting profession
Understanding the Accounting Profession
As a cornerstone of business operations, accounting involves a complex blend of technical knowledge and analytical skills. Accountants help organizations and individuals manage their financial records and make smart choices with their money.
What Accountants Do
Accountants’ duties may include preparing financial statements and reports, evaluating risk, and ensuring accuracy and compliance in record-keeping. They might also help develop organizational budgets and advise executives on financial decisions. By serving as financial stewards for businesses, organizations, and individuals, accountants ensure accuracy and integrity in financial reporting.
The work of accountants requires a blend of technical knowledge and communication skills, as they must be able to analyze financial data and present their findings effectively.
Types of Accounting Specializations
Accountancy encompasses many specializations, including tax accounting, financial accounting, and managerial accounting. Accountants can also specialize in specific economic sectors like healthcare, tech, or government. The diverse career paths available within the accounting profession allow individuals to choose areas that align with their interests and skills.
By understanding the various specializations and industries within accounting, individuals can make informed decisions about their career paths.
How to Become An Accountant: The Educational Path
Embarking on a career in accounting requires a solid educational foundation, which typically begins with a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field.
Most bachelor’s programs take four years to complete and entail about 120 credits. However, since Certified Public Accountant (CPA) candidates need 150 credits, some schools offer five-year courses of study that meet this credit requirement and allow students to earn their bachelor’s and master’s degrees concurrently.
Bachelor’s Degree Requirements
A bachelor’s degree in accounting or business administration with an accounting concentration is typically required to enter the accounting profession. The coursework for a bachelor’s degree in accounting usually includes:
- Financial accounting
- Cost accounting
- Taxation
- Auditing
- Business law
- Information systems

Master’s Degree Considerations
A master’s degree in accounting or taxation can help accountants qualify for more job opportunities. These degrees build advanced accounting knowledge and allow students to delve into specialized topics. A master’s degree usually takes about two years to complete.
| Degree Level | Typical Duration | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Bachelor’s | 4 years | 120 credits |
| Master’s | 1-2 years | 30-60 credits |
Accounting Coursework and Skills Development
Through accounting education, students develop critical skills beyond technical knowledge, including analytical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and ethical reasoning. These skills are essential for success in the accounting profession.
Essential Certifications for Accounting Professionals

In the accounting profession, certifications play a vital role in career advancement and demonstrating expertise. These credentials not only signify a level of competence but also enhance job prospects and career growth opportunities.
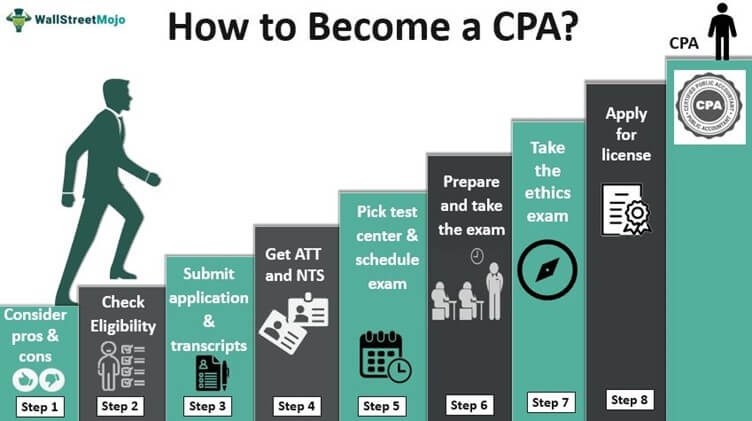
Certified Public Accountant (CPA)

The Certified Public Accountant (CPA) is one of the most prestigious certifications in the accounting field. To become a CPA, candidates must meet specific education requirements, pass the Uniform CPA Examination, and gain relevant work experience. The CPA exam is a four-part test that assesses a candidate’s knowledge in areas such as auditing, financial accounting, and taxation.
As noted by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), “The CPA certification is a mark of excellence that demonstrates a commitment to the accounting profession and a high level of expertise.”
“The CPA certification is a valuable asset for any accounting professional looking to advance their career.” – AICPA
Other Valuable Certifications
While the CPA is a widely recognized certification, other credentials can be beneficial for specialized accounting careers.
Certified Management Accountant (CMA)
The Certified Management Accountant (CMA) certification is ideal for professionals focusing on management accounting. It demonstrates expertise in financial planning, analysis, and decision-making.
Certified Internal Auditor (CIA)
The Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) certification is geared towards internal auditors, emphasizing their ability to evaluate and improve an organization’s risk management and internal controls.
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
The Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) certification is designed for professionals who audit, control, and monitor IT systems. It’s particularly valuable in today’s technology-driven business environment.
| Certification | Focus Area | Key Skills |
|---|---|---|
| CPA | Public Accounting | Auditing, Financial Accounting, Taxation |
| CMA | Management Accounting | Financial Planning, Analysis, Decision-making |
| CIA | Internal Auditing | Risk Management, Internal Controls |
| CISA | IT Auditing | IT Systems Audit, Control, Monitoring |
Continuing Education Requirements
To maintain their certifications, accounting professionals must complete continuing professional education (CPE) courses. These requirements ensure that certified professionals stay updated with the latest accounting standards, regulations, and best practices.
For instance, CPAs must complete a certain number of CPE hours every year to maintain their licensure. This commitment to ongoing education is crucial in the ever-evolving field of accounting.
Building Experience in the Accounting Field
Building a strong foundation in accounting requires hands-on experience. As we navigate the steps to become an accountant, it’s crucial to understand that theoretical knowledge is just the beginning. Practical experience is what sets aspiring accountants apart in a competitive job market.
We emphasize the critical importance of practical experience in developing accounting expertise and advancing in the profession. Internships, entry-level positions, and continuous learning opportunities are essential for growth.
Practical Experience through Internships
Internship opportunities provide a gateway to gaining industry experience. By working as interns, aspiring accountants can build professional skills and become familiar with the realities of working in the accounting field. Internships offer hands-on practice in a real accounting environment and can be a valuable source of professional connections.
- Internships can be found with accounting firms, corporations, government agencies, and non-profit organizations.
- Some students receive job offers at the companies where they intern, making internships a potential stepping stone to full-time employment.

Entry-Level Positions in Accounting
Typical entry-level accounting positions include staff accountant, junior auditor, and tax associate. Employers expect new graduates to have a solid educational foundation and be ready to apply their knowledge in real-world settings. These roles provide a foundation for future growth and specialization within the accounting field.
Advancing Your Accounting Career
As accountants gain experience, they progress from handling basic transactions to managing complex financial analyses and eventually supervising teams. Building a professional network within the accounting community is crucial for career advancement. This can be achieved through professional associations, mentorship relationships, and continuing education events.
By strategically building their experience, aspiring accountants can align their career trajectory with their long-term goals in the accounting profession. It’s about creating a path that is both fulfilling and challenging, with opportunities for continuous learning and growth.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
As we explore the financial aspects of becoming an accountant, it’s crucial to understand the salary expectations and job outlook in this profession. The accounting field offers a range of salary possibilities and career advancement opportunities.
Average Salaries by Position and Experience Level
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median salary for accountants and auditors in Illinois was $71,270 as of May 2020. Experienced professionals in the top 10% earned an average of $118,520 during this time. The salaries vary significantly based on experience and position.
| Position | Entry-Level Salary | Median Salary | Top 10% Salary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accountants and Auditors | $34,400 | $71,270 | $118,520 |
| Controllers and Financial Managers | – | $132,360 | $208,000+ |
Regional Salary Differences
Geographic location significantly impacts accounting salaries. For instance, controllers and other financial managers in Illinois earn a median salary of $132,360, with top earners making over $208,000. Regional differences and metropolitan areas with high demand for accounting professionals can substantially influence salary ranges.
Future Growth in the Accounting Profession
The job market for accountants is expected to grow, driven by the need for financial management and compliance services. As businesses continue to expand and regulatory requirements evolve, the demand for skilled accounting professionals is likely to increase.
Understanding these factors can help aspiring accountants make informed decisions about their career paths and how to position themselves for maximum earning potential in the field.
Conclusion
Becoming an accountant requires dedication and hard work, but the benefits of a career in accounting far outweigh the challenges. As we’ve outlined, the path to becoming an accountant involves a strategic combination of education, certification, and experience. By pursuing a bachelor’s degree in accounting, obtaining certifications like the CPA, and gaining practical experience, individuals can set themselves up for success in this field.
The accounting profession offers stability, diverse opportunities, and a competitive salary. With the impending accountant shortage, hiring conditions are likely to remain favorable for accounting professionals. We encourage prospective accountants to stay focused on their goals and to be prepared to adapt to the evolving demands of the profession.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, individuals can confidently pursue their accounting career goals and enjoy a rewarding and challenging career.
FAQ
What are the typical educational requirements for a career in accounting?
We typically require a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field, such as finance or business, to pursue a career in accounting. Some positions may also require a master’s degree or certifications like the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) designation.
What skills are essential for success in the accounting field?
We believe that essential skills for accountants include proficiency in financial accounting software, analytical and problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and strong communication skills. Additionally, skills in tax preparation, auditing, and financial management are highly valued.
How long does it take to become a Certified Public Accountant (CPA)?
We understand that the time it takes to become a CPA can vary depending on the state’s requirements and our individual circumstances. Typically, it involves completing a certain number of college credits, gaining relevant work experience, and passing the CPA exam.
What are the job prospects and salary expectations for accountants?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of accountants and auditors is projected to grow. We can expect a median annual salary ranging from $60,000 to over $120,000, depending on factors like location, experience, and industry.
Are there different types of accounting specializations?
Yes, we have various specializations within the accounting field, including financial accounting, managerial accounting, tax accounting, auditing, and forensic accounting. Each specialization requires unique skills and knowledge.
What is the importance of continuing education in the accounting profession?
We recognize that continuing education is crucial in the accounting field, as it helps us stay updated on changing regulations, laws, and industry standards. Many states require accountants to complete a certain number of continuing education hours to maintain their certifications.